*** IMPORTANT SHIPPING & DELIVERY NOTICE ***
Some international couriers continue to experience shipping delays.
We recommend you buy early and in bulk to avoid the impact of these delays.*** CELEBRATING 25 YEARS!!! ***
For 25+ years, we've been supporting a Healthy Body, Strong Spirit and Clear Mind!
Providing superior quality medicinal mushroom supplements
to customers in 74 countries around the world.Buy More & SAVE Big!
- Tap for Navigation
- Dietary Supplements ▼
- » Dr Alla's Cordyceps
- » Dr Alla's Lion's Mane
- » Dr Alla's Maitake
- » Dr Alla's Reishi
- » Dr Alla's Shiitake
- » Testimonials
- Symptoms Chart
- Get Advice ▼
- » FAQ
- » Health Consultations
- Dr Alla's Insights ▼
- » Medical Conditions
- » Mushroom Properties
- » Research Info ►
- » » Medical Quotes
- » » Reference Works
- » » Mushrooms - Why Special?
- About ▼
- » Dr Alla's Story
- » Testimonials
- » Trade Enquiries
- » Contact
- Customer Info ▼
- » Access My Account
- » Track My Order
- Navigation
- Dietary Supplements ▼
- » Dr Alla's Cordyceps
- » Dr Alla's Lion's Mane
- » Dr Alla's Maitake
- » Dr Alla's Reishi
- » Dr Alla's Shiitake
- » Testimonials
- Symptoms Chart
- Get Advice ▼
- » FAQ
- » Health Consultations
- Dr Alla's Insights ▼
- » Medical Conditions
- » Mushroom Properties
- » Research Info ►
- » » Medical Quotes
- » » Reference Works
- » » Mushrooms - Why Special?
- About ▼
- » Dr Alla's Story
- » Testimonials
- » Trade Enquiries
- » Contact
- Customer Info ▼
- » Access My Account
- » Track My Order
Any disorder of the nervous system is referred to as a Neurological Disorder.
There are three types of abnormalities that cause it:
- Structural
- Electrical
- Biochemical
The respective wide range of symptoms may manifest themselves in the brain, spinal cord or any other nerves throughout the body.
These symptoms can be isolated or combined.
Here are some examples:
- Altered levels of consciousness
- Confusion
- Loss of sensation
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness
- Pain
- Paralysis.
- Pins-and-needles sensation
- Poor coordination ability
- Seizures
In 2006 the World Health Organisation estimated that neurological disorders and their direct consequences affect as many as 1 billion people worldwide.
It also identified issues such as health inequalities and social discrimination/stigma as major factors contributing to the associated disability and suffering of affected people.
It is obvious that much more needs to be done in the health industry around the world to improve the diagnostic methods, treatment options and ways of providing the adequate care for these patients.
Let’s take a brief look into the structure and function of the Nervous System.
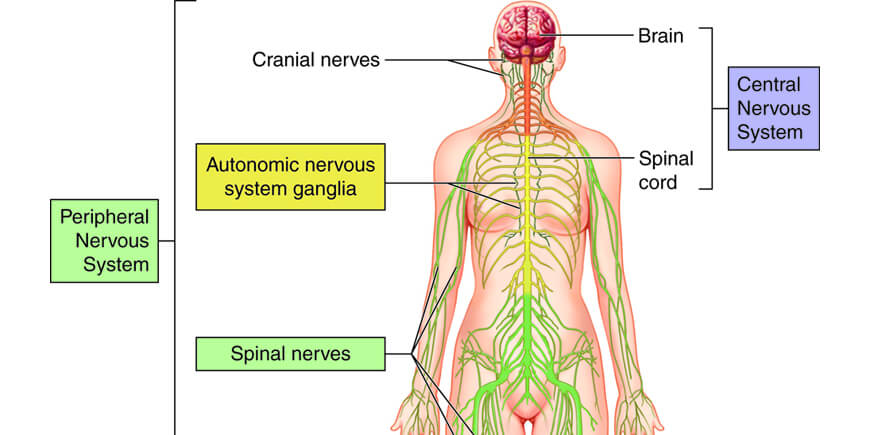
Nervous System is a highly complex structure.
It coordinates the body’s actions and sensory responses by transmitting signals back and forth between all organs and tissues in the body.
It consists of two main parts:
Central Nervous System (CNS) - contained in brain and spinal cord and protected by scull, vertebras and blood-brain barrier.
Examples:
- Caused by trauma - traumatic brain injury (tbi)
- Caused by infections – meningitis, brain abscess, spinal epidural infection
- Encephalitis
- Caused by degenerative disorders - alzheimer's, parkinson's, huntington's diseases
- Caused by structural defects - spina bifida, anencephaly, hypospadias
- Caused by tumours – developing in the brain, starting benign and then becoming malignant
- Caused by auto-immune disorders – abnormal immune response
- Caused by stroke – a blood clot blocks a blood vessel or when a blood vessel ruptures, causing blood to leak to the brain; if the brain cannot get enough oxygen and blood, brain cells can die, leading to permanent damage.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – consists of nerves and ganglia (a group of neuron cell bodies) and serves as a conduit between the brain, spinal cord and the rest of the body (all organs and tissues). It is not protected as CNS so it is exposed to injuries and toxins.
Examples:
- Caused by injuries or traumas - carpal tunnel syndrome, tarsal tunnel syndrome; caused by toxic damage occurred in cases of diabetes (diabetic neuropathy), alcohol, heavy metals or other toxins;
- Caused by autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, such as amyloidosis and sarcoidosis.
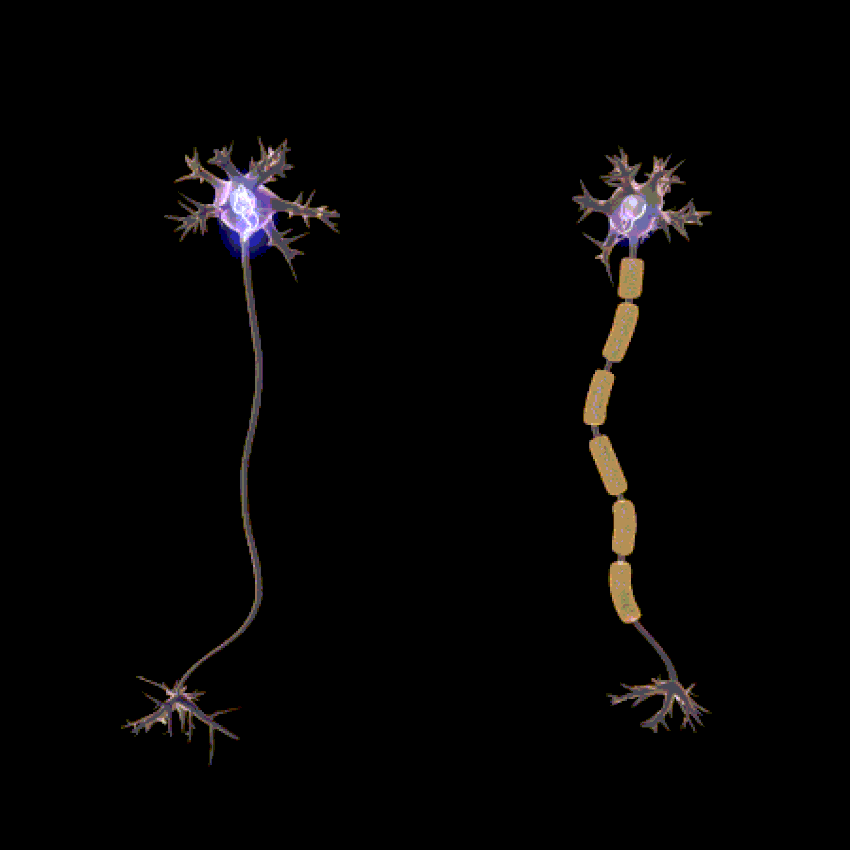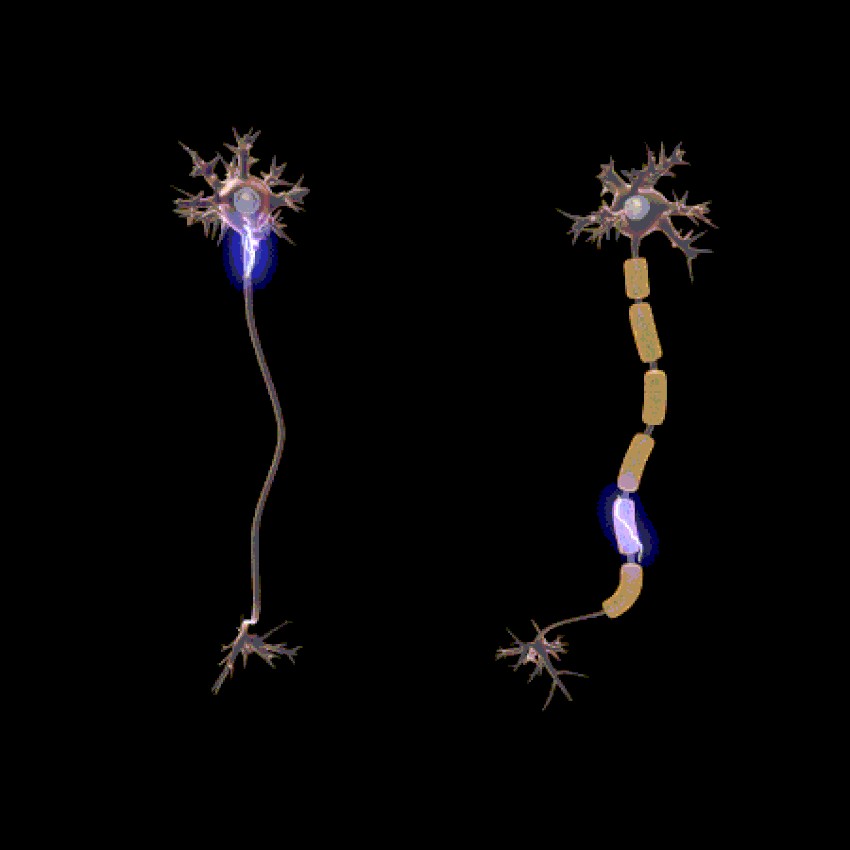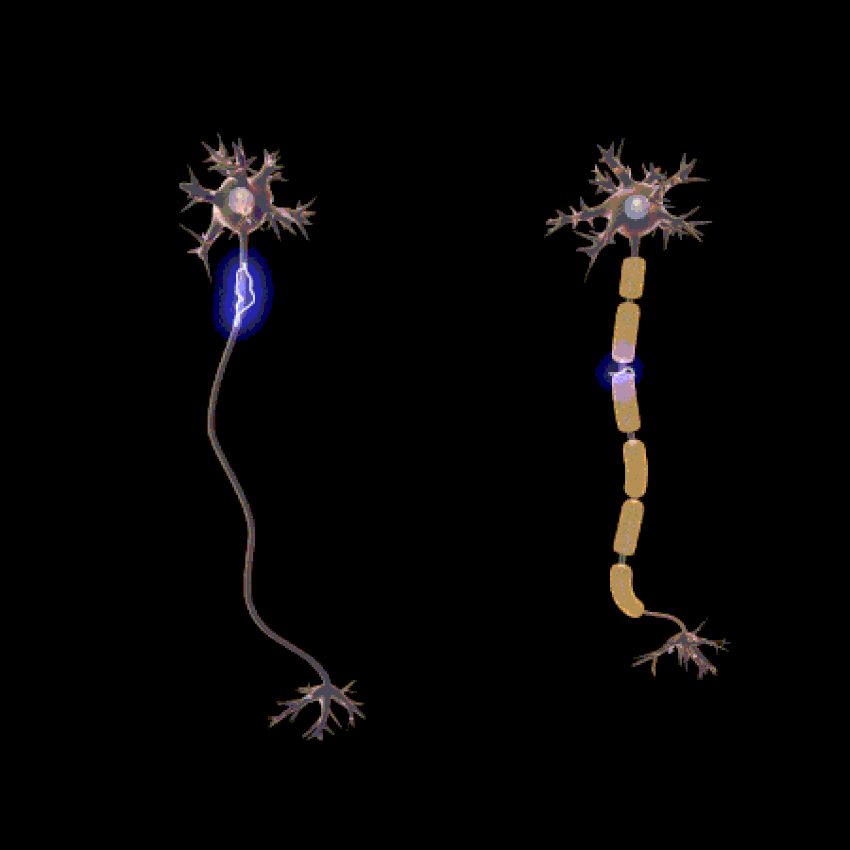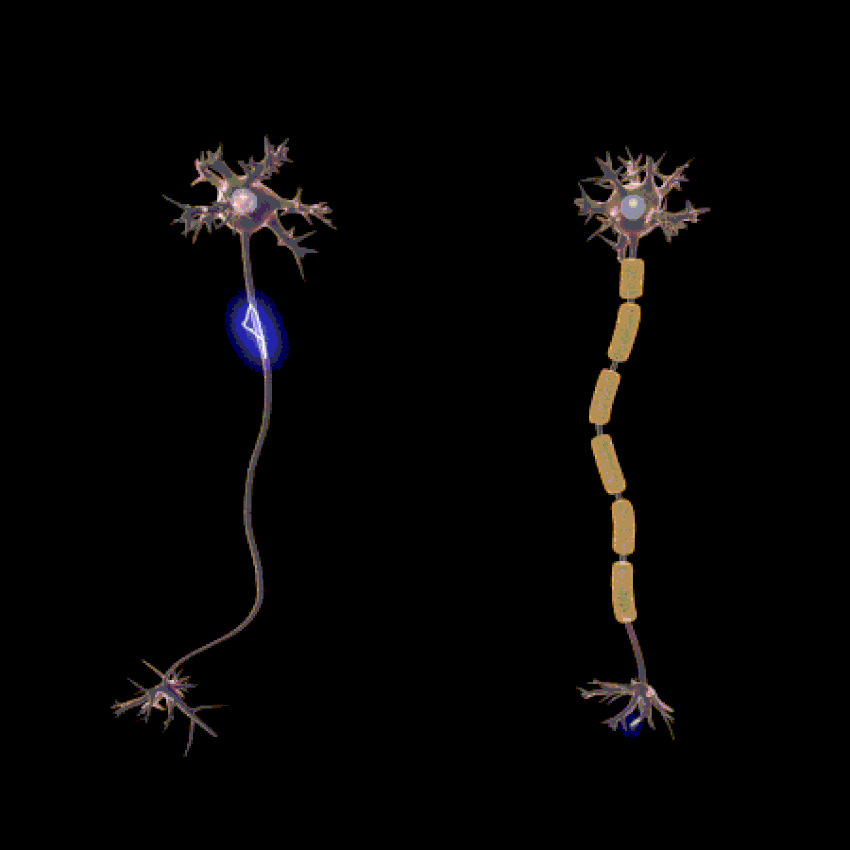
The function of the nervous system is determined by the presence of a special type of cells, called neurons. These neurons are structured in such a way that they are capable of sending signals rapidly and precisely to other cells throughout the body.
The signals are sent in the form of electrochemical waves traveling along the length of thin fibres called axions, which allow for chemicals called neurotransmitters to be released at nerve junctions (synapses).
The connections between neurons can form neural pathways or neural circuits and even large complex networks of nerves that create the perceptions of the environment and determine the behaviour or reaction of the body to the circumstances.
The causes of neurological disorders are most extensive, but can be summarised as related to:
- Autoimmune disorders
- Brain injury
- Celiac disease
- Cerebrovascular disorders
- Congenital disorders
- Environmental conditions
- Genetic disorders
- Gluten sensitivity
- Lifestyle conditions
- Lysosomal storage disease
- Malnutrition
- Metal poisoning
- Nerve injury
- Spine injury
- Toxic conditions
- Viral infections
There are several suggested treatment methods for neurological disorders that include but not limited to physiotherapy, environmental and lifestyle changes, dietary changes, pain management, prescription medications, specific therapeutic methods, surgeries.
It is most unfortunate that the mainstream practicing doctors and specialists are not aware of a natural product, a medicinal mushroom called Lion's Mane (Hericium erinaceus).
This magical mushroom contains one unique property that is essential for all patients suffering of any neurological disorders.
Lion’s Mane stimulates the synthesis of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and promotes the process of myelination.Myelin is a special protective or insulating layer made up of proteins and fatty substances and forms around all nerves, including brain and spinal cord nerves.
The main function of myelin is to protect and insulate the neurons and stimulate the quick and efficient transmission of the electrical impulses along the nerve cells. This allows for increased complex brain function processes.
The myelination processes are vital for increased speed of signals transmitted between the neurons and thus stimulating the brain function as well as the function of the entire nervous system, central and peripheral.
When the myelin is damaged, the transmission of the electrical impulses is slowed down or interrupted which manifests itself in severe neurological conditions, for example as seen in multiple sclerosis patients.
Medicinal mushroom Lion’s Mane triggers the activation of the Central and Peripheral nerve regeneration.
The chemical profile of Lion’s Mane extracts has been extensively researched by hundreds of scientific institutions worldwide. The unanimous conclusion is that Lion’s Mane (Hericium erinaceus) has an undeniable ability to stimulate the Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and thus boost the regeneration process of the nerves on the cellular level.
Here is just one example reported by Kawagishi and his co-researchers.
Extracts of H. erinaceus induced the expression of neurotrophic factors such as nerve growth factor (NGF) in astrocytes.
Hericium erinaceus (300 mg/kg, continuously fed for 14 days after surgery) significantly decreased the size of the cerebral infarcts one day after the occlusion.
In another study, a double-blind trial was conducted with 50- to 80-year-old Japanese men and women diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment in order to examine the efficacy of oral administration of H. erinaceus, for improving cognitive impairment, using a cognitive function scale based on the revised Hasegawa Dementia Scale (HDS-R).
The subjects in the H. erinaceus group took four 250 mg tablets containing 96% of Yamabushitake / Lion’s Mane dry powder three times a day for 16 weeks. Cognitive function scale scores increased with the duration of intake.
Lion’s Mane is regarded the most potent medicinal mushroom when it comes to boosting the brain function and stimulating the repair / regeneration of the damaged nerves.
The wonderful fact is that there are no side-effects from taking Lion’s Mane for a long period of time. Personally, I am taking it for well over 30 years on daily basis and so are many of my clients. A huge number of studies report that Lion’s Mane should be promoted as functional food.
But there are three more mushrooms that should be added to it: Cordyceps, Maitake and Reishi. These medicinal mushrooms contain bio-active properties that when combined with Lion’s Mane tremendously increase the potency and the overall benefits for patients dealing with neurological problems.
Recommended Medicinal Mushrooms:
CONTACT INFO
021 227 9922 (NZ)
+64 21 227 9922sales@medimushrooms.co.nz
Skype: alla.kiroshka
We ship globally to 74 countries and locally to all regions of New Zealand. Local shipping destinations include Auckland, Bay of Plenty, Gisborne, Hawke's Bay, Manawatu-Whanganui, Northland, Taranaki, Waikato, and Wellington on the North Island. As well as Canterbury, Marlborough, Nelson, Otago, Southland, Tasman, and West Coast on the South Island.

Top NZ cities and towns we ship to include Alexandra, Arrowtown, Ashburton, Auckland City, Blenheim, Bluff, Cambridge, Christchurch, Cromwell, Dannevirke, Dargaville, Dunedin, Eltham, Feilding, Gisborne, Gore, Greymouth, Hamilton, Hastings, Havelock North, Hawera, Hibiscus Coast, Hokitika, Huntly, Invercargill, Kaikoura, Kaitaia, Kāpiti Coast, Katikati, Kawerau, Kerikeri, Levin, Lower Hutt, Manukau City, Marton, Masterton, Matamata, Morrinsville, Motueka, Napier, Nelson City, New Plymouth, Ngaruawahia, North Shore, Oamaru, Otaki, Palmerston North, Paraparaumu, Picton, Porirua, Queenstown, Rolleston, Rotorua, Stratford, Taupo, Tauranga, Te Awamutu, Te Puke, Thames, Timaru, Tokoroa, Upper Hutt, Waihi, Wanaka, Warkworth, Wellington City, Wellsford, Westport, Whakatane, Whanganui, Whangarei, Whitianga.
Copyright © 2004 - 2024 MediMushrooms International Ltd
DISCLAIMER: The information on this website has been researched, reviewed and presented with all due care.
Nevertheless, the content is provided for general education and information only and should not be relied upon in making,
or refraining from making, any decision. It is NOT intended to replace medical advice from a healthcare professional.
All users are urged to seek advice from a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis, treatment and answers to their medical questions.
Use products as directed. If symptoms persist, please see your healthcare professional.Specific results expressed herein are not typical. Individual results will vary.